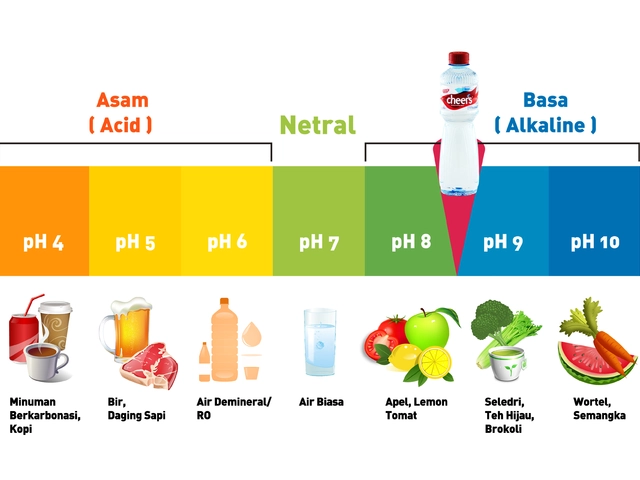
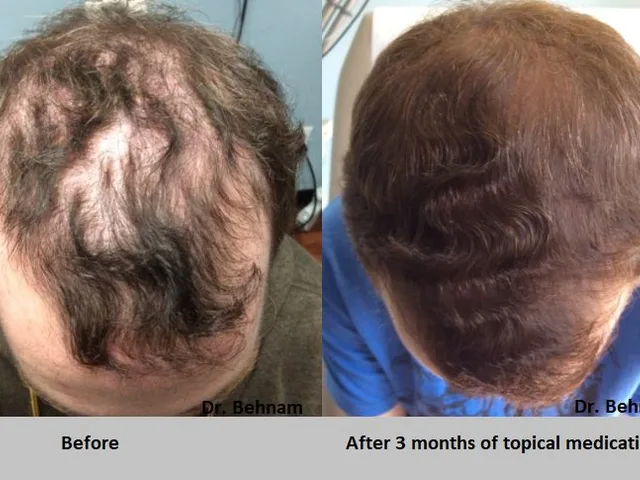
Amikacin: How It Works, When It’s Used, and What to Watch For
When working with Amikacin, an injectable aminoglycoside antibiotic for serious gram‑negative infections. Also known as Akamin, it binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit and stops bacterial protein synthesis. In practice, Aminoglycoside antibiotics, a class that includes gentamicin and tobramycin share a similar mechanism but differ in dosing schedules and toxicity profiles. Because they target Gram‑negative bacteria, organisms like Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter, physicians often reserve them for hospital‑acquired infections where other drugs fail. Understanding the link between drug resistance, the ability of bacteria to survive antibiotic exposure and proper dosing is crucial; misuse can drive resistant strains and increase side effects.
Key Considerations When Using Amikacin
First, Dosage and administration, usually calculated by weight and kidney function determine both efficacy and safety. Monitoring peak and trough levels helps avoid nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, the two major adverse effects of aminoglycosides. Second, patients with existing kidney issues should have dose adjustments; otherwise, the drug can cause irreversible hearing loss. Third, combining amikacin with other nephrotoxic agents, such as vancomycin, raises the risk of kidney damage, so clinicians often stagger therapies or choose alternatives. Finally, when you need to obtain amikacin or similar antibiotics online, verify the pharmacy’s credentials, check for a valid prescription requirement, and compare prices to avoid counterfeit products.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that walk through buying cheap generic medications safely, understanding antibiotic resistance, and managing side effects of powerful drugs like amikacin. Whether you’re looking for dosage tables, safety checklists, or tips on spotting legitimate online pharmacies, the collection ahead covers the practical angles you’ll need.

A detailed side‑by‑side comparison of Mikacin (Amikacin) injection with gentamicin, tobramycin, vancomycin, ceftriaxone, and imipenem, covering efficacy, safety, dosing, cost and when to choose each.
Chris Gore Oct 6, 2025